What are indirect manufacturing costs?

Accordingly, the unit cost of production would be measured using the newest or oldest inventory items. Business News Daily provides resources, advice and product reviews to drive business growth. Our mission is to equip business owners with the knowledge and confidence to make informed decisions. The same cost can be labeled as indirect in one industry and direct in another.
Top 7 Differences Between Direct and Indirect Costs
Direct costs are almost always variable because they are going to increase when more goods are produced. Employee wages may be fixed and unlikely to change over the course of a year. However, if the employees are hourly and not on a fixed salary then the direct labor costs can increase if more products are manufactured.
Examples of indirect costs
Indirect costs are infeasible to allocate to each unit of product or service since these costs are used in multiple manufacturing activities and can’t be assigned to a single unit. Once NEH issues an award, it is not obligated to make adjustments due to increases in your organization’s indirect cost rate agreement. We encourage companies to review both their direct and indirect costs on a monthly basis. You need to keep track of your indirect costs because if they are increasing, you may need to price your goods differently—or quickly improve your efficiency in order to achieve a higher gross margin.
- For example, if an employee is hired to work on a project, either exclusively or for an assigned number of hours, their labor on that project is a direct cost.
- Profit margins serve as a good measure of how efficient and profitable a company is at providing its products and services.
- The tools used in construction projects — especially those that are reusable across different projects —are considered indirect costs.
- Indirect costs are costs that are not directly accountable to a cost object (such as a particular project, facility, function or product).
- By harnessing digital tools, construction firms can assist in bringing accuracy, foresight, and agility to their financial management.
Formula: How to Calculate Direct and Indirect Costs?

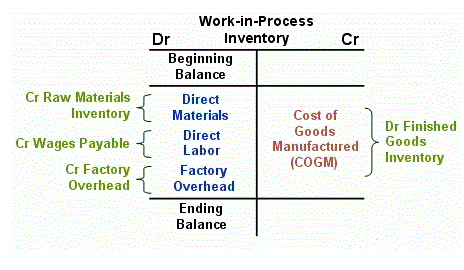
Indirect manufacturing costs are a manufacturer’s production costs other than direct materials and direct labor. Indirect manufacturing costs are also referred to as manufacturing overhead, factory overhead, factory burden, or burden. Continuous monitoring of direct and indirect expenses provides valuable insights into the efficiency of business operations to identify areas for improvement and cost optimization. For example, if an employee is hired to work on a project, either exclusively or for an assigned number of hours, their labor on that project is a direct cost.
What are Indirect Costs of a Cost Object?
At sustainable bedding retailer Ethical Bedding, founder and CEO James Higgins admits he monitors business costs more or less ‘constantly’. “It’s absolutely imperative to know your product costs and running costs because that’s how you know which levers to pull from a cost perspective, and how those costs are linked to revenue and ultimately profit,” he says. Modified Total Direct Costs, excludes equipment, capital expenditures, rental costs, tuition remission, scholarships and fellowships, participant support costs and the portion of each subaward in excess of $25,000. It is used mainly by manufacturing companies that produce several product lines or work with a number of businesses. The selling, general and administrative expenses to go to market are $10,000, $10,000 and $5,000, respectively.
Indirect costs include expenses such as the salaries of the project manager and administrative staff, renting office space to manage the project, and insurance and legal fees. Companies should review their indirect costs regularly and draw comparisons with prior periods. For example, they can compare their costs in January 2023 with those of January https://www.bookstime.com/ 2022. They can also compare the current year with the last fiscal year, as well as the actual numbers with those in the budget. This would allow business owners to spot trends and address cost issues as they arise. Just like direct costs, indirect costs can be numerous, and will typically differ considerably from one industry to another.
Data Analytics and Predictive Tools
- Certain government agencies might allow you to explain why indirect costs should be funded, too, but the decision to grant funding is at their discretion.
- Hence, mastering cost management is an important part of running and growing a business.
- They can integrate various aspects of construction project management, including budgeting and financial oversight.
- The financial analyst should also keep a close eye on the cost trend to ensure stable cash flows and no sudden cost spikes occurring.
Also referred to as manufacturing overhead, factory burden, factory overhead, and manufacturing support costs. Identifies any limitations on the use of the rates, the basis of accounting, rate specific information (such as indirect costs are also referred to as costs. fixed or provisional rates), the use of the NICRA by other federal agencies, and other information. Allocating costs is important and useful because it helps you understand whether you are pricing your goods competitively.

Correct allocation of direct and indirect costs leads to more accurate and transparent budgeting, forecasting and cash flow planning, as well as reporting for management and financial purposes. For example, factory overhead costs can be apportioned to each unit produced by the total number of products manufactured, or based on the number of hours it took to manufacture each product. This helps a company to calculate the overhead cost per unit so that prices can be set accordingly to ensure a profit is made on each product even after incorporating all indirect expenses.
Overhead Costs
Understanding direct costs and indirect costs is important for properly tracking your business expenses. Ultimately, determining a reasonable indirect cost rate requires careful analysis of the specific circumstances of a project and the construction company involved. Generally, a reasonable indirect cost rate falls within the range of 10% to 20% of the total direct costs of a project. A reasonable indirect cost rate can vary depending on a variety of factors, such as the type of construction project, the location, and the size of the construction company.
In an example of a car manufacturer, the materials like steel, plastic or glass used in the car production line are classified as direct costs. Indirect costs, although often overshadowed by their direct counterparts, hold significant sway over a project’s bottom line. Ensuring their meticulous assessment and proactive oversight not only safeguards profitability but also establishes the foundation for successful project execution. In construction, both indirect and soft costs denote expenses that aren’t directly tied to the physical construction activities. When an entity accepts a grant, such as government funding, the funding guidelines typically stipulate what qualifies as a direct versus indirect cost, along with any threshold amounts for each cost type. Understanding the true total cost of producing goods and services enables a business to make sound decisions, particularly in the areas of pricing, budgeting, operational efficiency, and taxation.
Otváracie hodiny
Otváracie hodiny:
Pondelok – Piatok: 10:00 – 22:00
Sobota – Nedeľa: 11:00 – 22:00
Opening hours
Opening hours:
Monday – Friday: 10:00 to 22:00
Saturday – Sunday: 11:00 – 22:00